Animal-free research trends & how the US is embracing the shift
The trend of animal-free research is becoming a priority strategy for many countries, with the United States leading the way through a series of wide-ranging reforms. From the FDA Modernization Act to technologies like organ-on-chip and AI toxicity models, the US is not only “saying no to mice” but also setting a new scientific standard for the future. This article will analyze how the US is turning policy into action and action into new standards.
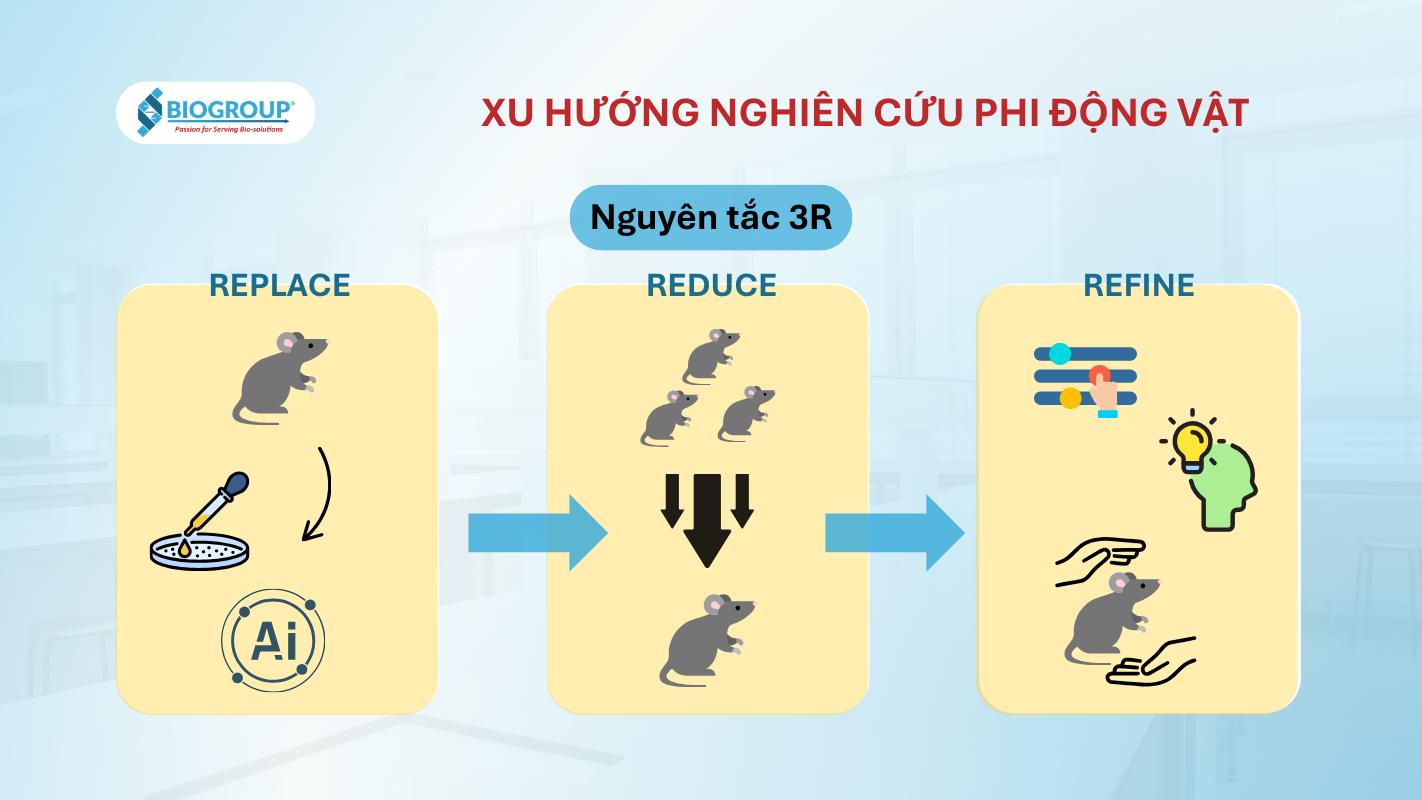
The 3R principle of animal-free research
Contents
ToggleAnimal-free research is gaining global attention
In the vaccine and pharmaceutical industries, the use of animal testing is gradually being replaced by in vitro (test tube-based), in silico (computer simulation), and other advanced technologies. This shift is driven by both policy requirements and technological advances, aiming to improve accuracy, shorten research timelines, and ensure ethical standards in research. The 3R principle (Replace, Reduce, Refine) is increasingly emphasized in the laws and research guidelines of many countries. New technologies such as organ-on-chip, 3D cell cultures, and AI-based simulations are proving to predict human safety and efficacy better than traditional animal models. For example, organ-on-chip devices, which are microscopically lined with human cells, simulate the physiological functions of organs like the lungs and liver, making drug testing in environments closer to human physiology possible. Meanwhile, computer models can predict toxicity based on biochemical data, and omics methods (genomics, proteomics, etc.) provide an animal-free approach to assess mechanisms of action.
First, we will analyze in detail the trend of replacing animal testing in human vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, veterinary drugs, and veterinary vaccines in the United States. This will help us better understand the advanced technologies being applied in this developed country. The data, roadmap, and updated references up to 2025 are provided from government sources, research organizations, and industry.
National policies driving animal-free research
The US is making historic shifts to reduce reliance on animal testing through changes in laws and guidance from regulatory agencies. In late 2022, the US Congress passed the FDA Modernization Act 2.0, amending federal law to eliminate the mandatory requirement for animal testing of new drugs. The new law allows “certain alternative methods,” such as cell models or computer simulations, to demonstrate preclinical safety and efficacy. In 2023, Congress further allocated $5 million to the FDA to develop animal-free research methods and proposed the FDA Modernization 3.0 Act to ensure regulations accept animal-free data for drug evaluations. By 2025, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) is set to release the “Roadmap to Reducing Animal Testing,” with plans to gradually phase out animal testing requirements for drug evaluations, particularly for monoclonal antibodies. According to the FDA’s statement in April 2025, the agency will encourage data from alternative methods, including AI models predicting toxicity, cell-line testing, and organ-on-chip (collectively referred to as New Approach Methods, or NAMs), in clinical trial applications for Phase I trials. The FDA is moving toward a “NAM-based default” in the coming years, using animal testing only as an exception when new methods cannot answer scientific questions. The agency’s long-term goal is to eliminate animal toxicity testing for monoclonal antibodies and eventually all drug types, replacing it with a “NAM toolbox” that integrates human cell models and computational models. Other US agencies are also taking strong stances. In 2025, the National Institutes of Health (NIH) launched an initiative prioritizing human-based research platforms to reduce animal use in NIH-funded projects. The NIH plans to establish a specialized office (Office of Research Innovation, Validation, and Application – ORIVA) to advance new technologies like organ-on-chip, computer models, and human data usage. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) also set a goal of cutting mammalian toxicity testing by 30% by 2025, with plans for complete elimination by 2035 (though the 2035 goal was later adjusted; efforts to reduce animal use continue). See the related article “NIH Halts Funding for Animal Research – What Are the Alternative Approaches?” In the field of vaccines, the United States has abolished some traditional animal testing methods. For example, the “abnormal toxicity test” (formerly required for each batch of vaccine tested on guinea pigs) was eliminated by the USP and FDA around 2018, following WHO recommendations. The FDA and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) have also issued guidelines to replace animal-based vaccine potency tests. Since 2011, the FDA has approved the use of a botulinum potency test developed by Allergan on cell cultures, replacing the LD50 test on mice. The USDA created a series of in vitro ELISA tests to evaluate the efficacy of Leptospira vaccines in veterinary medicine, replacing the fatality tests on hundreds of hamsters for each vaccine batch. These replacement tests have been formalized into standards (Supplemental Assay Methods) and have significantly reduced the number of animals used annually. Additionally, the USDA has adjusted regulations to reduce animal use in other tests further. For example, in 2013, they allowed a 50% reduction in hamster use in the Leptospira vaccine potency challenge by removing the reverse titration requirement, and in 2017, extended the shelf life of reference standards in vaccine tests to 15 years to avoid repeated testing on large animals. Overall, the United States is entering a “new era” of non-animal testing. There is strong political and scientific consensus on this: a survey showed that 86% of Americans support replacing animal testing with more modern methods. Both the government and the research community recognize that human-based technologies (such as human cell models, AI, and clinical data) will better predict human responses, accelerate drug development, and save costs compared to animal models. As a result, a series of laws, budgets, and programs were introduced between 2019 and 2025 in the U.S. to change the scientific culture, integrating alternative methods into regulations and training scientists to evaluate non-animal data.
Trends and technological advances in animal-free research in the US
The U.S. is a leader in developing many animal-free technologies (NAMs) for drug and vaccine safety testing:
Organ-on-chip and Microphysiological systems
The NIH/NCATS developed the “Tissue Chip” program in the early 2010s to create human-physiological models on chips. Organ-on-chip systems (lung chips, liver chips, gut chips, etc.) are being tested to screen drug and vaccine toxicity with higher accuracy than animal models. The FDA is also collaborating with institutes like the Wyss Institute at Harvard and has recognized that these systems can detect toxicity missed by animal tests and reflect human responses directly. In 2025, the FDA will allow some pharmaceutical companies to submit safety data primarily based on organ-on-chip and organoid models in their approval dossiers, with guidelines to encourage and expedite review if alternative data is sufficiently robust.
Artificial intelligence and in silico modeling
The application of AI/Machine Learning for predictive toxicity is growing rapidly. The FDA encourages using computer models to simulate drug distribution in the body and predict side effects based on molecular structure. Software for pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics (PBPK modeling) and AI networks trained on big data (including omics data from humans) help forecast toxicity and harmful doses without animal testing. Since 2015, the EPA and NIH have had the Tox21 program, collaborating with the Department of Energy to use robotic testing on cells and machine learning algorithms to screen thousands of chemicals for toxicity signals without animal use. AI models are proving increasingly reliable, with studies showing that AI algorithms can sometimes outperform mouse models in predicting specific toxicities by avoiding inter-species physiological differences.
3D cell culture and organoid models
3D cell culture technology to create miniature organs (organoids) is booming in the US. Many startups and labs have developed 3D brain models, liver models, and “tumors-on-a-plate” to test cancer drugs. These organoids replicate the structure and function of human organs, allowing for more complex in vitro drug and vaccine testing than traditional flat cell lines. For example, the NIH funded a project to create 3D lung models infected with viruses to test flu and COVID-19 vaccine candidates. This helps identify toxicity on human tissue early, before animal or human trials. The FDA is also encouraging the integration of organoid data into preclinical safety data packages. By 2025, the FDA aims for each major toxicity area to have a feasible NAM alternative, such as 3D liver models and computational predictions for liver toxicity or immune system models-on-chip for immune toxicity.
Alternatives in vaccine testing
In addition to drug research, the US is gradually replacing animal-based tests for vaccine lot testing. The USDA led the development of immunological tests, replacing disease challenge methods: for example, four ELISA tests for antigen detection have been approved to assess Leptospira vaccine potency, eliminating the need to infect hamsters with bacteria during veterinary vaccine lot testing. Similarly, rabies testing in mice has been improved by removing certain lethal criteria to reduce animal use and recommending anesthesia and pain relief for animals in still-required tests. Notably, in 2024, a European method, the Leukocyte Response Assay (MAT), developed by the VAC2VAC EU project, was reviewed by the FDA/USDA to replace fever induction testing on rabbits. This MAT method has proven to be as sensitive in detecting pyrogens (fever-causing substances) as the rabbit test. The US is shifting animal-free research from theory to practice with clear policies and pioneering technologies. The goal for the next few years is to make animal-free research the new standard, improving both the speed and safety of vaccine and pharmaceutical development for humans and animals. The US is asserting its global leadership in modern science management, encouraging the industry to invest more in humane and more effective testing platforms. Contact information:
- Website: https://biogroupvietnam.com/public/lien-he
- Hotline: +84 963 621 421
- Email: info@biogroupvietnam.vn
Refer to STEMCELL Technologies’ animal-free research solutions
Reference
- Jordbruksverket. (2023, December 20). 50 years of replacing animal experiments. https://jordbruksverket.se/languages/english/swedish-board-of-agriculture/animals/the-swedish-3rs-center/news/arkiv/2023-12-20-50-years-of-replacing-animal-experiments
- Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine. (n.d.). FDA’s plan to replace animal testing begins new era of drug testing, says doctors group. https://www.pcrm.org/news/news-releases/fdas-plan-replace-animal-testing-begins-new-era-drug-testing-says-doctors-group
- National Institutes of Health. (n.d.). NIH to prioritize human-based research technologies. https://www.nih.gov/news-events/news-releases/nih-prioritize-human-based-research-technologies
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (n.d.). FDA announces plan to phase out animal testing requirement for monoclonal antibodies and other drugs. https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-announces-plan-phase-out-animal-testing-requirement-monoclonal-antibodies-and-other-drugs
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (n.d.). Animal testing alternatives. https://www.fda.gov/media/186092/download
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2021, January 19). EPA new approach methods: Efforts to reduce use of animals in chemical testing. https://19january2021snapshot.epa.gov/research/epa-new-approach-methods-efforts-reduce-use-animals-chemical-testing
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. (2021, January 19). EPA new approach methods: Efforts to reduce use of animals in chemical testing. https://19january2021snapshot.epa.gov/research/epa-new-approach-methods-efforts-reduce-use-animals-chemical-testing
- ALTEX. (n.d.). Complete elimination of animal testing by 2035. https://www.altex.org/index.php/altex/announcement/view/358
- Plant Based News. (n.d.). South Korea stops toxicity animal testing. https://plantbasednews.org/news/science/south-korea-stops-toxicity-animal-testing
- National Toxicology Program. (n.d.). Vaccine testing – Acceptance of cell-based assays for botulinum neurotoxin products. https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/whatwestudy/niceatm/test-method-evaluations/biologics-and-vaccines/vaccine-testing
- National Toxicology Program. (n.d.). Vaccine testing – USDA in vitro assays and SAMs revision 2017. https://ntp.niehs.nih.gov/whatwestudy/niceatm/test-method-evaluations/biologics-and-vaccines/vaccine-testing
Categories
- Blog (55)
- Training & Webinar (28)
- Virtual Booth (1)
- New Products & Technologies (45)
- News (41)
- Recruitment (11)