Isolate Cells From Blood
New Products & Technologies
Isolate Cells From Blood
Blood can be processed in various ways to obtain cell preparations, which can then be used directly in biological assays or further processed to isolate more specific cell subsets.
Whole blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells (RBCs; or erythrocytes), platelets, and nucleated white blood cells, also referred to as leukocytes. The leukocytes can be further categorized into mononuclear cells and polymorphonuclear cells (or granulocytes). Here we outline different techniques to obtain peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), polymorphonuclear cells, leukocytes, or specific cell subsets.
Deplete Red Blood Cells
Isolation of specific cell types for functional studies or downstream assays may require RBC depletion during the cell preparation step. There are several ways to deplete RBCs, including:
- RBC lysis with ammonium chloride
- Dextran sedimentation or HetaSep™
- Immunomagnetic cell separation (e.g. EasySep™ RBC Depletion Reagent)
- Hypotonic lysis
After the RBC depletion is complete, the resulting sample will contain all nucleated white blood cells (leukocytes) that can be used for downstream assays or further processed to isolate a specific cell subset.
Prepare Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
PBMCs include lymphocytes (i.e. T cells, B cells, and NK cells), monocytes, and dendritic cells, and are defined as white blood cells with round nuclei. Preparation of a PBMC fraction from whole blood is a common step prior to the isolation of specific immune cell subsets. The most common PBMC isolation method involves using a density gradient medium (e.g. Ficoll™ or Lymphoprep™) and centrifugation. This method takes advantage of the differences in density between the cells in blood and the density gradient medium.
Whole blood is first diluted with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and then carefully layered over the density gradient medium. During centrifugation, the cells with higher densities (i.e. granulocytes and erythrocytes) sediment through the density gradient medium. The PBMCs settle at the interface between the density gradient medium and the plasma, from which they can be carefully collected.
Tip: Although this method can be time-consuming, particularly when working with multiple samples, it can be significantly sped up by using SepMate™ tubes.
PBMCs can also be immunomagnetically isolated directly from blood without centrifugation or lysis using the EasySep™ Direct Human PBMC Isolation Kit. This fast isolation method results in purified PBMCs in as little as 20 minutes and works on whole blood, cord blood, bone marrow, buffy coats, and leukapheresis products. Alternatively, you can purchase frozen PBMCs.
After obtaining PBMCs, immunomagnetic cell separation and other cell isolation techniques can be used to isolate specific cell subsets.
Prepare Peripheral Blood Polymorphonuclear Cells
Polymorphonuclear cells, also known as granulocytes, are a collection of immune cell subsets with enzyme-containing granules that can be released upon cell activation. To obtain a population of polymorphonuclear cells from whole blood, you can do any of the following:
- Perform density gradient centrifugation followed by ammonium chloride lysis. You can then isolate specific granulocyte populations such as neutrophils, basophils, or eosinophils using immunomagnetic cell separation technologies.
- Directly isolate granulocytes from blood, without lysis or density centrifugation, using EasySep™ Direct cell isolation technology. This approach allows you to quickly and easily obtain pan-granulocytes or one of the more specific granulocyte subsets (e.g. neutrophils, basophils, or eosinophils).
Prepare Buffy Coats
A buffy coat is a concentrated suspension of leukocytes and results when erythrocytes and plasma are separated from the leukocyte fraction by low speed centrifugation.
This procedure allows you to concentrate large sample volumes and remove donor-specific soluble serum factors, which helps to reduce donor variability. A buffy coat can be prepared from whole blood or bone marrow and can be used as the starting sample for the isolation of specific cell populations using immunomagnetic cell separation technologies such as EasySep™.
Isolate Specific Cell Subsets Directly from Whole Blood
Some cell separation technologies (e.g. EasySep™ Direct and RosetteSep™) allow you to isolate specific cell subsets directly from whole blood without needing to isolate PBMCs first.
Isolate Cells from Apheresis Products
Apheresis is a process in which whole blood is drawn from an individual, separated into components, and reinfused back into the individual with a certain component (e.g. plasma, platelets, or leukocytes) removed.
Leukapheresis is a form of apheresis where leukocytes are collected from a donor's circulating blood. Leukopaks, which are enriched leukapheresis products containing higher concentrations of leukocytes per volume compared to whole blood or buffy coat, are an ideal starting source of mononuclear cells that can be used for immune cell isolation. Depending on the method you choose, you can prepare a Leukopak for cell separation by either isolating the PBMC fraction from it or simply depleting RBCs prior to cell isolation.
Plateletpheresis is another form of apheresis where thrombocytes, commonly called platelets, are separated from the rest of the blood. This process can include a leukoreduction step to remove leukocytes from the platelet fraction, resulting in leukocyte reduction system chambers/cones containing a high concentration of leukocytes in a small volume. LRSCs are usually discarded after routine donor plateletpheresis, but are an excellent source of leukocytes that can be used as an alternative source of PBMCs for research purposes.
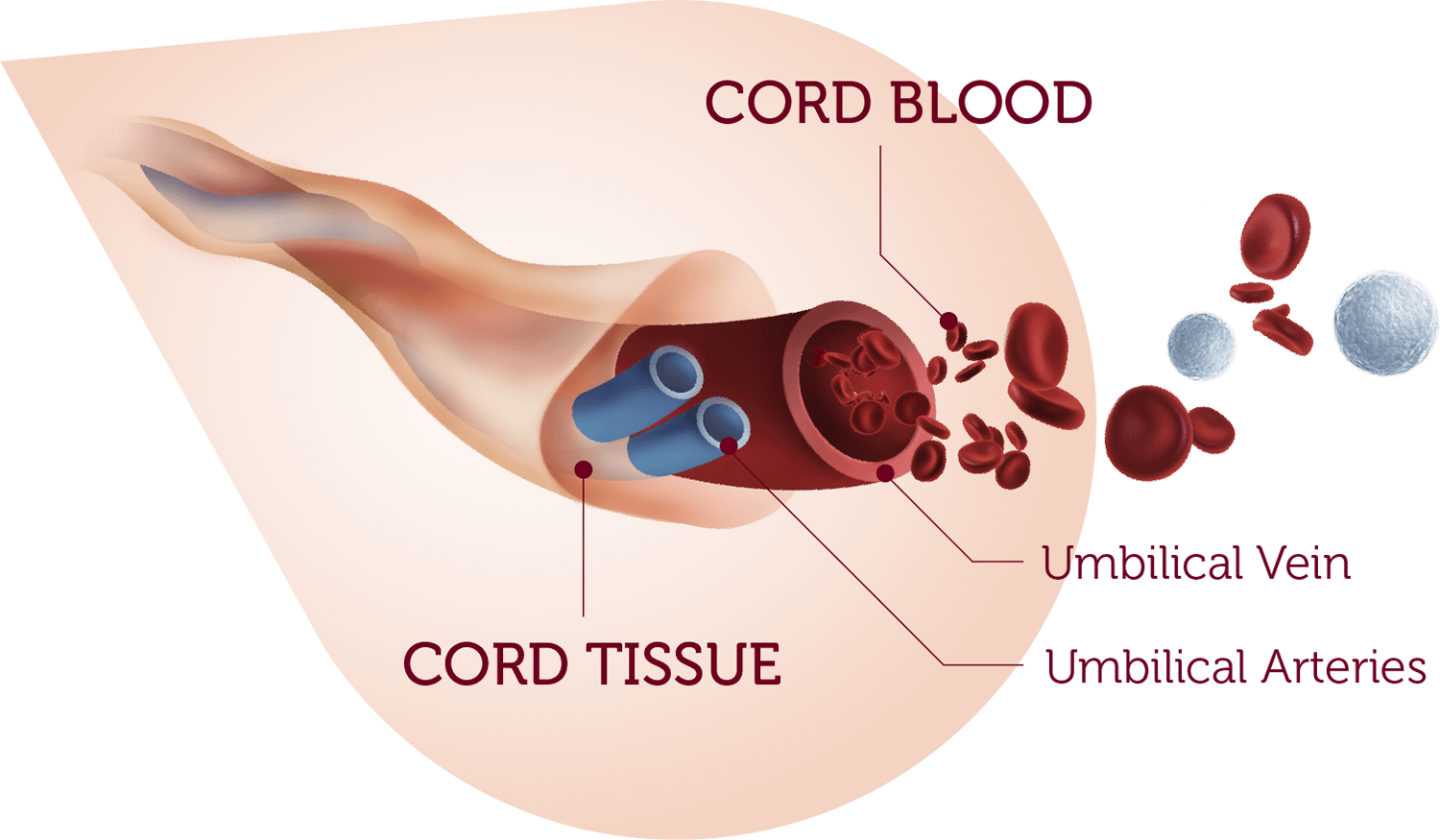
Isolate Cells from Cord Blood
Cord blood can be collected from the placenta and umbilical cord after birth. Immune cells found in cord blood can be isolated to study early-life immune responses. To isolate specific cell populations from cord blood, you can first prepare mononuclear cells by using density gradient medium (e.g. Lymphoprep™) and centrifugation, or you can simply deplete RBCs.
Depleting RBCs from cord blood requires special considerations. Standard ammonium chloride lysis may be too harsh for the hematopoietic or immune progenitor cells contained in cord blood. Alternative methods for RBC depletion may be better suited to removing RBCs from this sample source (e.g. EasySep™, ErythroClear™, HetaSep™).
Another factor to keep in mind is that cord blood can have very high platelet counts, which may facilitate the formation of clots. It is important to use suitable anticoagulants, like acid citrate dextrose (ACD) or EDTA, and to follow the manufacturer's instructions pertaining to cord blood when processing samples.
(Source: STEMCELL Technologies - Canada)







.png)